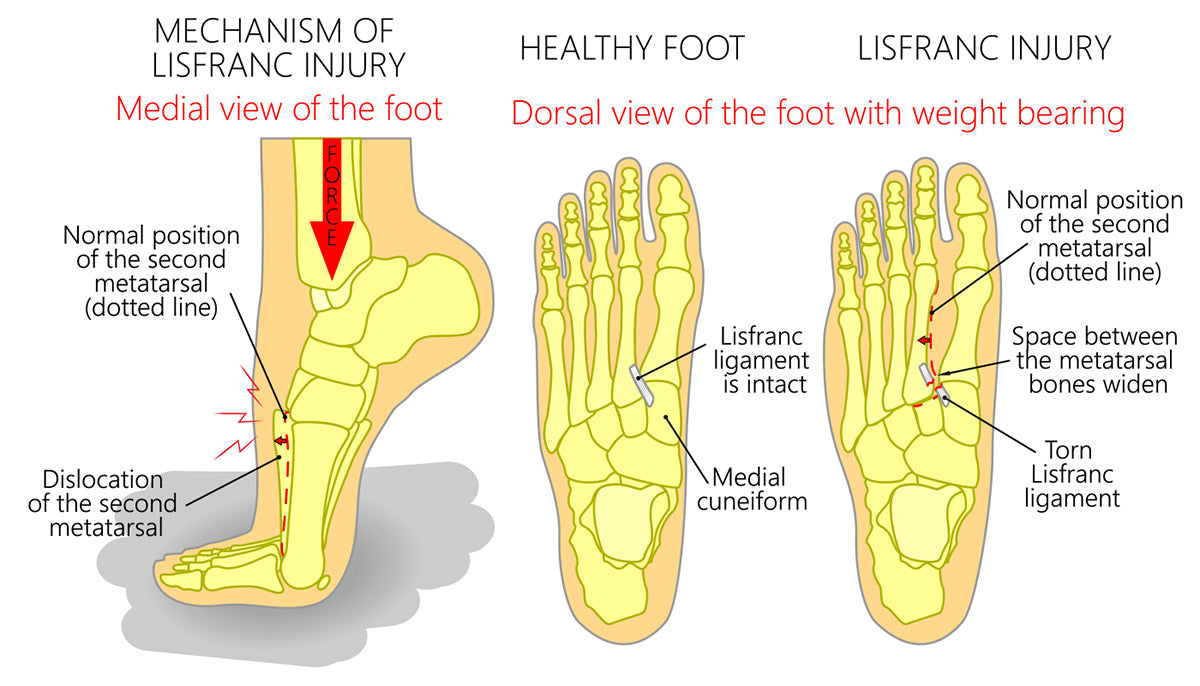
A Lisfranc injury refers to a disruption of the tarsometatarsal (TMT) joints in the midfoot. These joints connect the bones of the midfoot where the Lisfranc joint is located to the bones of the forefoot and are responsible for maintaining and stabilizing the arch of the foot. Lisfranc injuries can affect the top, bottom, or side of the foot, depending on the severity and location of the injury. It may cause swelling and bruising, pain and tenderness. The injuries can range from mild to severe and may involve ligament sprains, fractures, or dislocations.
What is the most common cause of Lisfranc fracture?

Lisfranc injuries are often caused by trauma, such as by direct impact when a heavy object is dropped on the foot or impact from a vehicular accident. A severe twist of the foot, such as during a fall or athletic activity, can also result in Lisfranc injury. Lisfranc injuries are relatively uncommon, but they can occur in various situations, and certain factors may increase the risk of experiencing such an injury.
The individuals at risk for Lisfranc injuries include:
- Athletes: Lisfranc injuries are frequently seen in athletes, particularly those involved in sports that carry a risk of foot trauma or those that require sudden changes in direction or pivoting, such as football, soccer, and basketball.
- Motor Vehicle Accidents: Trauma resulting from a car accident, especially if there is significant force applied to the midfoot, can lead to Lisfranc injuries.
- Falls: A fall from a height or a direct impact on the foot, especially if the foot is twisted during the fall, can cause Lisfranc injuries.
- Occupational Risks: Certain occupations that involve heavy machinery, equipment, or the risk of falling objects may increase the likelihood of Lisfranc injuries.
- Previous Foot Conditions: Individuals with pre-existing foot deformities or conditions, such as flat feet or a high arch, may be at a higher risk of Lisfranc injuries due to altered foot mechanics.
- Improper Footwear: Wearing shoes that do not provide proper support or do not fit well can contribute to foot injuries, including Lisfranc injuries. For dress shoes that are comfotable and provide great support view our collection.
- Gender and Age: Lisfranc injuries are more common in men than in women, and they often occur in young to middle-aged adults.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions that weaken bones or ligaments, such as osteoporosis, may contribute to an increased risk of Lisfranc injuries.
It's important to note that while these factors may increase the risk, Lisfranc injuries can occur in anyone, and sometimes they may result from unpredictable accidents. Prompt and accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for the best outcomes, regardless of the cause. If there is a suspicion of a Lisfranc injury, seeking medical attention as soon as possible is advised.
How do you diagnose a Lisfranc Injury?
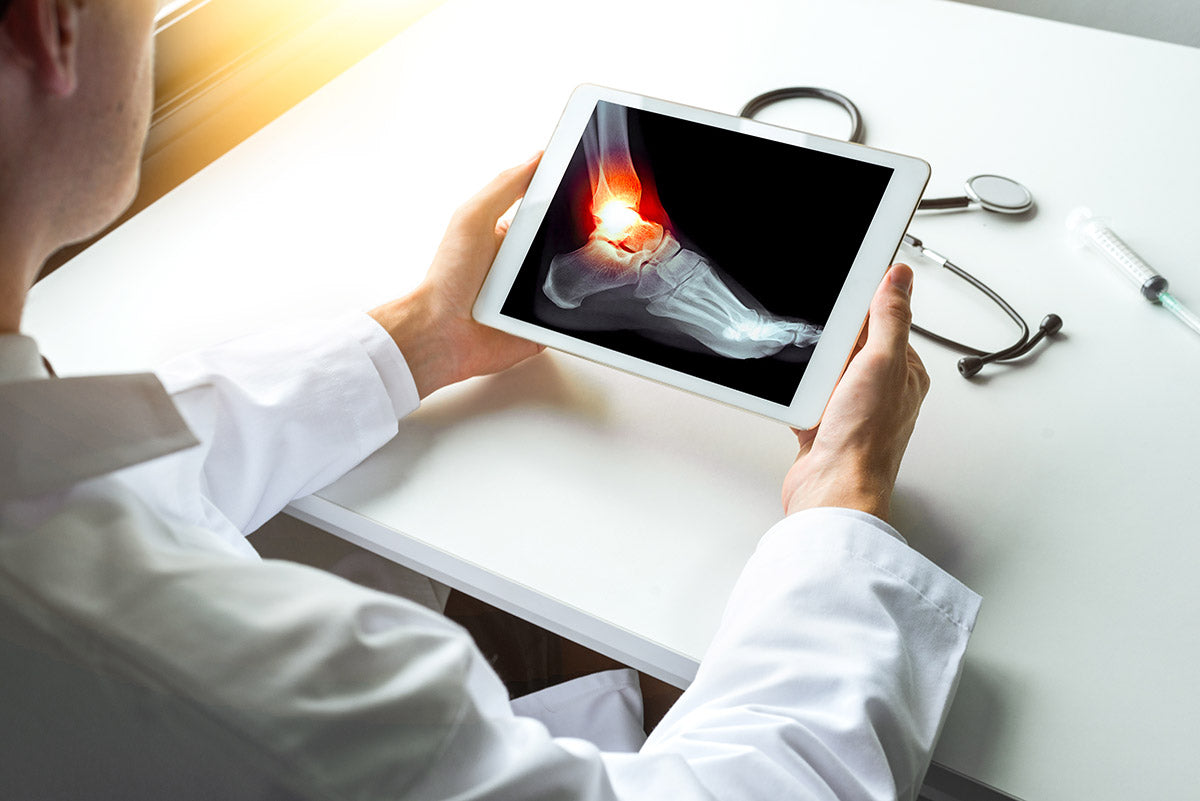
Diagnosing Lisfranc injuries can be challenging because symptoms can be subtle, and X-rays may not always reveal the full extent of the injury. A doctor will assess the foot for tenderness, swelling, and stability. X-rays can help identify fractures or dislocations, but more advanced imaging like CT scans or MRIs might be needed for a detailed view.
How do you treat a Lisfranc Injury?
Treatment depends on the severity of the injury. Mild injuries may be treated with conservative measures: rest, ice, elevation, and immobilization in a cast or boot. Rehabilitation, including physical therapy, is crucial to restoring strength and function. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be taken to relieve pain and inflammation. Severe injuries, including fractures or significant joint displacement, often require surgical intervention.
Surgery for Lisfranc injuries is typically tailored to the specific nature and severity of the injury. The goals of surgery are to realign and stabilize the affected joints, allowing for proper healing and minimizing the risk of long-term complications. Here are some common surgical approaches used for Lisfranc injuries:
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF): This is a common surgical technique where the surgeon makes an incision over the affected area, repositions the displaced bones, and then uses screws, plates, or other fixation devices to stabilize the joint. The choice of hardware depends on the specific characteristics of the injury.
- Primary Arthrodesis (Fusion): In cases where there is significant joint damage or instability, the surgeon may opt for fusion of the affected joints. This involves removing damaged cartilage and fusing the bones together using screws, plates, or other fixation devices. While this limits joint motion, it can provide stability and relieve pain.
- Joint Reconstruction: In some cases, especially if ligaments are severely damaged, joint reconstruction may be necessary. This can involve the use of grafts or other techniques to repair or replace damaged ligaments, restoring stability to the joint.
What is the success rate of Lisfranc surgery?

The choice of surgical technique depends on factors such as the specific bones involved, the extent of the injury, and the overall health of the patient. After surgery, a period of immobilization is often required to allow for proper healing. Rehabilitation, including physical therapy, is crucial to regaining strength and function. Patients should follow their healthcare provider's advice regarding weight-bearing exercises and other aspects of recovery.
It's important for individuals with Lisfranc injuries to consult with orthopedic surgeons experienced in foot and ankle care to determine the most appropriate surgical approach for their specific case. Early intervention and proper surgical management can significantly impact the long-term outcomes and reduce the risk of complications such as arthritis and chronic pain.
How long does a Lisfranc sprain take to heal?

The outcome for all Lisfranc patients varies based on the severity of the injury, the type of treatment, and how well the patient follows the rehabilitation plan. With prompt and appropriate treatment, many people with Lisfranc injuries can regain normal function. However, severe injuries, injuries left untreated, or injuries not properly treated can result in long-term foot problems and may lead to other complications. For more common foot pain issues check out our in depth foot pain guide.